Heat Resistant Steel
Heat Resistant Steel refers to the steel which is capable of resist scaling at temperature above 500 �C. The heat resistant steel grades are not exposed to mechanical stress, owing to its oxidized layer which is created throughout the developing process when the steel is exposed to gentle and strong oxidizing conditions at elevated temperatures.
This steel is adherent and its intense oxide layers provides the heat resistance of the material. It is capable of upholding processes when exposed, either continuously or erratically, to operating temperatures which result in metal temperatures in excess of 650 �C. The heat resistance of the steel depends on its chromium, silicon and aluminum content.
Heat resistant steels can be classified on the basis of their microstructure as follows:
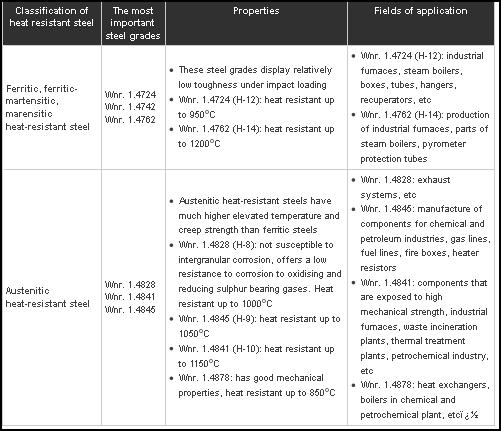
High Temperature Steels
 Owing to its higher resistance to chemical and mechanical degradation at elevated temperatures, high temperature steels is extensively demanded in the market. Due to their characteristics such as corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, hydrogen brittleness and creep resistance these are ideal choice for high temperature working environments.
Owing to its higher resistance to chemical and mechanical degradation at elevated temperatures, high temperature steels is extensively demanded in the market. Due to their characteristics such as corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, hydrogen brittleness and creep resistance these are ideal choice for high temperature working environments.
The steel is classified on the basis of its micro-structure, which can be ferritic-austenitic (duplex), ferritic, austenitic and martensitic. The structure of steel grade is determined by its chemical composition.