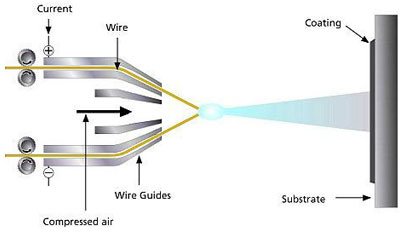
Wire Arc Spray
This form of thermal spraying uses wire material as a feed stock. An electric arc is used as the heat source. As the wires are fed towards each other, an electric arc is struck between the wires creating a temperature of around 4,000°C.
This temperature causes the tips of the wire to melt and once molten state, a stream of compressed air or inert gas is used to atomise and accelerate the feed metal towards the substrate.
Characterestics of Wire Flame Spray
| Material Form | Wire |
| Heat Source | Electric Arc |
| Flame Temperature (°C) | 3600 to 4000 |
| Gas Velocity (m/sec) | < 300 |
| Porosity (%) | 10 to 15 |
| Coating Adhesion (MPa) | 28 to 42 |
Advantages:
- Coatings with good characteristics can be achieved
- Two different wires can be used simultaneously to produce a pseudo alloy
- Cored wires are also available producing coatings with unique properties
- Applying coating to large areas is easier by this process
- Used for dimensional restoration due to higher deposit efficiency
Disadvantages:
- Coatings achieved are not dense and have porosity of up to 15%
- Good suface preparation is very essential for good bond strength
- Coatings limited to materials available in wire form with low melting tempertaure


